Remember when chatbots could only answer “What’s your return policy?” with a pre-written script?
Those days are over.
In 2025, the customer support landscape has shifted from scripted, limited chatbots to autonomous AI agents that understand context, take real action, and solve problems without human help. The difference isn’t just technical jargon—it’s about results.
According to Grand View Search, the AI agents market is reaching $7.6 billion in 2025. It is growing at approximately 45% annually, nearly double the 23% growth rate of the traditional chatbot market.
This isn’t hype; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses automate customer interactions.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover:
✅ AI agent vs chatbots: The core differences
✅ When to use chatbots vs AI agents for your business
✅ How AI agents compare to AI assistants, LLMs, and ChatGPT
✅ Real-world use cases and implementation strategies
✅ Step-by-step guidance on building your own AI agent chatbot with LangChain
Let’s dive in.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is an AI tool that simulates human-like conversations through text or voice. It follows preset rules or scripts to handle simple, repetitive tasks like answering common FAQs.
How Traditional Chatbots Work
Chatbots are usually powered by rule-based engines, decision trees, or basic NLP models that rely on keyword matching and intent classification. They operate on simple if-then logic.
- User asks: “What are your business hours?”
- Chatbot responds: “We’re open Monday-Friday, 9 AM to 5 PM.”
2 Types of Chatbots in 2025
- Rule-Based Chatbots
- Follow decision trees
- Limited to predefined scenarios
- Cannot handle unexpected queries
- AI-Powered Chatbots
- Use NLP for natural conversations
- Understand casual language
- Remember parts of a conversation within a session
Key Characteristics of Chatbots
AI chatbots provide answers and information, react to individual messages, have limited memory, and stay within the chat interface
What chatbots CAN do:
- Answer FAQs 24/7
- Guide users through predefined workflows
- Collect basic information (name, email, preferences)
- Reduce repetitive support tickets
What chatbots CANNOT do:
- Execute multi-step tasks independently
- Integrate with backend systems to take action
- Remember context across multiple sessions
- Adapt to complex, unpredictable scenarios
Real-World Example
Imagine a customer asks an e-commerce chatbot:
“Do you have this shoe in size 8?”
The AI chatbot checks inventory or directs users to the returns policy. If the user asks to change the delivery address or request a refund, the bot hands off to a human or provides the correct form link..
The chatbot informs, but doesn’t act.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a smart, autonomous assistant built on LLMs, gen-AI, and advanced NLP. It understands context, processes information, and executes goal-driven tasks.
As a result, businesses see less manual effort and better, faster support.
How AI Agents Work
An AI agent is an autonomous system that can perceive its environment, make decisions, learn, and act on your behalf to achieve a specific goal.
Think of it this way:
Chatbot = Digital Assistant
AI Agent = Digital Worker
Core Capabilities of AI Agents
AI agents have memory to remember past interactions and user history. They also use a reasoning engine to analyze data, make evidence-based decisions, and apply contextual awareness to handle complex, multi-step tasks.
What AI agents CAN Do?
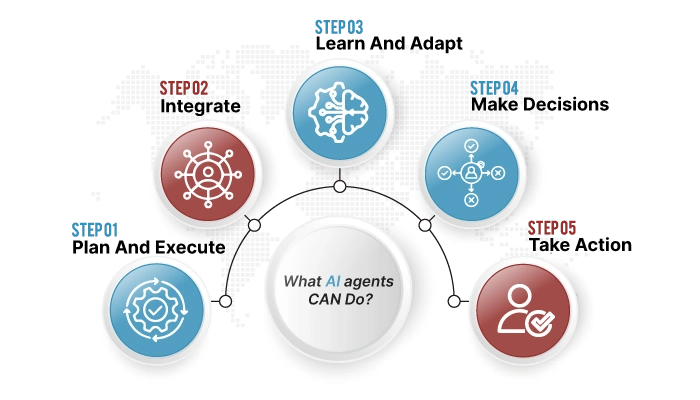
- Plan and execute multi-step workflows autonomously
- Integrate with CRMs, databases, and external APIs
- Learn and adapt from previous interactions
- Make decisions based on real-time data analysis
- Take action without waiting for human approval
Real-World Example of an AI Agent
Same scenario, customer wants a refund:
A strong AI agent can check the order, issue a refund, send a replacement, and close the loop, with no human involvement.
The AI agent completes the task end-to-end.
AI Agent Architecture
A language model powers the agent’s brain. It can fetch real-time data. It can recall previous context. And it can act across different systems.
Components:
- Perception: Monitors systems, databases, and user inputs
- Reasoning: Analyzes context and determines next actions
- Memory: Retains conversation history and user preferences
- Action: Executes tasks via API integrations
AI Agent vs Chatbot: 5 Key Differences
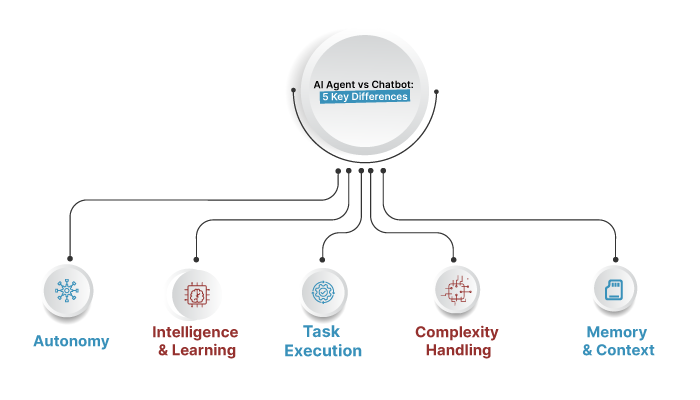
Chatbots are primarily reactive; they respond within predefined flows. Agents are goal-directed and can plan steps, choose tools, and iterate until a goal is reached
1. Autonomy
The biggest difference is autonomy. A chatbot follows a script, but an AI agent can think, plan, and carry out multi-step tasks on its own.
Chatbot:
- Waits for user prompts
- Responds based on pre-programmed rules
- Cannot initiate actions independently
AI Agent:
- Acts autonomously to achieve objectives
- Plans and executes workflows without manual triggers
- Operates continuously in the background
2. Intelligence & Learning
Chatbot:
- Even AI chatbots offer limited responses and can only execute simple support tasks
- Requires manual updates to improve
- Limited contextual understanding
AI Agent:
- AI agents learn from data, adjust their responses based on past interactions, and act on their own to meet set goals.
- Continuously improves through machine learning
- Deep contextual awareness across sessions
3. Task Execution
Chatbots typically fetch information or hand it off to a human or system. Agents connect to tools and APIs to take actions such as search, file operations, code execution, and data updates..
Chatbot:
- Provides information only
- Cannot execute tasks in external systems
- Limited to conversational interface
AI Agent:
- AI agents handle multi-step workflows, prioritize requests, update records in real time, and escalate issues when needed. It does it all with minimal human input.
- Integrates with CRMs, ERPs, and business tools
- Completes end-to-end processes
4. Memory & Context
Chatbots often reset context or keep only a short transcript. Agents maintain state over longer horizons, preserving conversation and tool context across runs..
Chatbot:
- Chatbots can’t retain memory across sessions, and any “learning” typically requires manual updates
- Every conversation feels like starting over
- Limited to a single-session context
AI Agent:
- Remembers user history, preferences, and past interactions
- Builds on previous conversations
- Maintains state across multiple touchpoints
5. Complexity Handling
Chatbots follow tidy paths but struggle with multi-step tasks that require back-and-forth with tools. Agents decompose tasks, chain tools, and even delegate to other agents..
Chatbot:
- Best for straightforward, single-intent queries
- Struggles with ambiguous or complex requests
- Cannot adapt to unexpected scenarios
AI Agent:
- Handles multi-step, cross-system workflows
- Adapts to changing requirements dynamically
- Breaks down complex goals into actionable steps
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Comparison Table:
| Feature | Chatbot | AI Agent |
| Primary Function | Provides information and answers | Takes action and completes tasks |
| Autonomy | Reactive—waits for user input | Proactive—acts independently |
| Intelligence | Rule-based or basic NLP | LLM-powered with reasoning capabilities |
| Memory | Limited to a single session | Retains context across sessions |
| Task Execution | Cannot execute external tasks | Integrates with systems to complete workflows |
| Learning | Manual updates required | Continuous learning from interactions |
| Use Cases | FAQs, lead capture, basic support | Refunds, bookings, workflow automation |
| Complexity | Simple, predefined scenarios | Multi-step, adaptive processes |
| Integration | Standalone chat interface | Connects to CRMs, APIs, and databases |
| Best For | High-volume, repetitive queries | Complex, goal-oriented tasks |
AI Agent vs AI Assistant: How They Compare
Many people confuse AI agents with AI assistants. While they share similarities, there are important distinctions.
What is an AI Assistant?
AI assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant let users perform tasks using natural, voice-based commands.
They respond to requests, set reminders, answer questions, and control smart devices.
Key Differences
AI Assistant:
- User-initiated interactions
- Focuses on personal productivity
- Executes tasks based on explicit commands
- Limited to predefined integrations
AI Agent:
- Can operate autonomously without prompts
- Focuses on business workflows and automation
- Makes independent decisions to achieve goals
- Deeply integrated with enterprise systems
Example Comparison
AI Assistant (Siri):
- “Hey Siri, set a reminder for my meeting at 3 PM.”
- Action: Sets a reminder.
AI Agent (Customer Support Agent):
- Detects a failed payment for a subscription.
- Autonomous Actions:
- Sends a payment failure notification
- Offers alternative payment methods
- Schedules a follow-up if unresolved
- Updates CRM with customer interaction
Bottom line: AI assistants are personal helpers, while AI agents are business process automators.
AI Agent vs LLM: Understanding the Distinction
Another common confusion: Are AI agents and LLMs the same thing?
What is an LLM?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is the AI technology that powers text generation and understanding. Examples include:
- GPT-4
- Claude
- Gemini
- LLaMA
LLMs are trained on massive datasets to predict and generate human-like text.
Key Differences
LLM:
- Core function: Processes and generates text
- Scope: Language understanding and generation
- Action: Responds—doesn’t execute tasks
- Example: GPT-4 generates a customer support email
AI Agent:
- Core function: Uses LLMs as the reasoning engine
- Scope: End-to-end task completion
- Action: Plans, decides, and executes workflows
- Example: An AI agent drafts the email, sends it, updates the CRM, and schedules a follow-up
Relationship Between LLMs and AI Agents
LLM = Engine
AI Agent = Complete System
An AI agent uses an LLM for natural language understanding and reasoning, but adds:
- Memory (to retain context)
- Tools (to integrate with systems)
- Autonomy (to act independently)
Real-World Analogy
- LLM = Car engine (generates power)
- AI Agent = Complete car (engine + wheels + steering + navigation)
You need the engine to move, but the engine alone won’t get you to your destination.
Use Cases: When to Use AI Agents vs Chatbots
Choosing between an AI agent and a chatbot depends on your business needs, complexity, and budget.
When to Use Chatbots
Chatbots are great at automating simple tasks and providing quick responses. They handle high-volume customer queries with ease. They also work well in industries that rely on structured interactions and predefined workflows.
Best Use Cases:
- E-commerce
- Chatbots announce daily offers directly in the chat window, personalizing deals based on browsing history or past purchases
- Answer product availability questions
- Guide customers through checkout
- Healthcare
- Healthcare chatbots ensure support is always available
- Book appointments
- Provide symptom checkers
- Share basic health information
- Lead Capture
- Chatbots can respond to human-written sales messages through WhatsApp, website embeds, or email
- Collect contact information
- Qualify leads with basic questions
- FAQs & Knowledge Base
- Answer repetitive questions
- Provide instant responses 24/7
- Reduce support ticket volume
When to Use AI Agents
AI agents work best for customer service tasks, excel at outbound calling campaigns, and also function as helpful agent copilots. AI agents handle fluid, natural conversations. They use dynamic reasoning to solve problems.
They take direct action by connecting to backend systems. This integration allows them to complete tasks automatically.
Best Use Cases:
- Customer Support Resolution
- Process refunds and returns end-to-end
- Update account information across systems
- Escalate complex issues based on severity
- Verify orders and trigger replacements
- Sales Automation
- AI agents find potential leads automatically from your CRM or other sources.
- They qualify these leads using your specific criteria.
- The agents then write personalized outreach messages for each lead.
- Follow-ups happen automatically without manual input.
- Sales outreach agents schedule meetings when leads respond.
- All interactions are logged directly in your CRM system.
- IT Operations
- In IT operations, a chatbot acknowledges an incident, while an agent runs diagnostics, summarizes impact, and applies a safe fix window with approvals
- Automate system monitoring
- Execute remediation workflows
- Workflow Automation
- Coordinate multi-step processes across departments
- Update records in real-time
- Generate reports and analytics
- Personalized Customer Experiences
- Businesses using AI agents achieve quicker resolutions, reduce operational costs, and deliver a better customer experience.
Decision Matrix: Chatbot or AI Agent?
| Scenario | Recommended Solution |
| Answering FAQs | Chatbot |
| Lead capture and qualification | Chatbot |
| Processing refunds/returns | AI Agent |
| Multi-system workflow automation | AI Agent |
| Appointment scheduling | Chatbot (simple) / AI Agent (complex) |
| Personalized recommendations | AI Agent |
| IT troubleshooting | AI Agent |
| Product availability checks | Chatbot |
6 Benefits of AI Agents Over Traditional Chatbots
Why are businesses rapidly adopting AI agents in 2025? Here are the key advantages:
1. End-to-End Problem Resolution
Chatbot: “Here’s a link to our refund policy.”
AI Agent: Processes the refund, confirms completion, and updates all systems.
While a chatbot might answer politely, an agent closes the loop
2. Autonomous Operation
AI systems do more than reply. They manage full workflows across multiple platforms and tools.
- No need for constant human oversight
- Operates 24/7 without breaks
- Scales effortlessly during peak times
3. Continuous Learning
Businesses that use AI agents see faster issue resolution. They also reduce operating costs. Overall, customer experience improves significantly.
- Adapts to new scenarios automatically
- Optimizes responses based on outcomes
- Reduces error rates over time
4. Cross-System Integration
Businesses using AI agents see faster issue resolution, reduced operating costs, and better customer experiences.
Example workflow:
- Customer requests a refund
- The agent verifies the order in the e-commerce platform
- Initiates refund via payment gateway
- Updates CRM with interaction details
- Sends confirmation email
- Notifies the finance team
5. Superior Customer Experience
Companies that implement AI agents experience faster support, lower expenses, and improved customer satisfaction.
Metrics
- Faster resolution times: Issues solved in minutes, not hours
- Higher satisfaction: Customers appreciate completed tasks, not just information
- Reduced escalations: Fewer cases requiring human intervention
6. Cost Efficiency
While AI agents may have higher initial setup costs, they deliver greater ROI by:
- Handling more complex tasks
- Reducing the need for human agents on repetitive issues
- Preventing costly errors through automated validation
How to Build an AI Agent Chatbot (GitHub Resources)
Ready to build your own AI agent chatbot? Here’s a practical roadmap with GitHub resources.
Step 1: Choose Your Tech Stack
Core Components:
- LLM Provider: OpenAI (GPT-4), Anthropic (Claude), Google (Gemini)
- Agent Framework: LangChain, AutoGPT, LlamaIndex
- Backend: Python (FastAPI, Flask) or Node.js
- Database: PostgreSQL, MongoDB (for memory/context)
- Deployment: Docker, AWS, Azure
Step 2: Set Up Your Development Environment
bash
# Install core dependencies
pip install langchain openai python-dotenv
# For LangChain agent development
pip install langchain-openai langchain-community
Step 3: Build Your First AI Agent
Basic AI Agent Structure:
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory# Define tools your agent can usetools = [Tool(name=“Search”,func=search_function,
description=“Useful for searching information”
),
Tool(
name=“Calculator”,
func=calculator_function,
description=“Useful for mathematical calculations”
)
]
# Initialize LLM
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
# Add memory for context retention
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key=“chat_history”)
# Create agent
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=“conversational-react-description”,
memory=memory,
verbose=True
)
# Run agent
response = agent.run(“Process a refund for order #12345”)
Top GitHub Repositories for AI Agents
- LangChain
- URL: github.com/langchain-ai/langchain
- Stars: 80k+
- Best for: Building production-ready AI agents with tool integration
- AutoGPT
- URL: github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
- Stars: 160k+
- Best for: Autonomous task execution and goal-oriented agents
- BabyAGI
- URL: github.com/yoheinakajima/babyagi
- Stars: 19k+
- Best for: Task-driven autonomous agents
- AgentGPT
- URL: github.com/reworkd/AgentGPT
- Stars: 29k+
- Best for: Browser-based AI agents with UI
- OpenAI Agents SDK
- URL: Check OpenAI documentation
- Best for: Production-grade agent workflows with built-in tools
Step 4: Add Essential Features
Memory & Context:
python
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
# Retains last N interactions
memory = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=5)
Tool Integration:
python
# Example: CRM integration tool
def update_crm(customer_id, status):
# Connect to CRM API
response = crm_api.update_customer(
id=customer_id,
status=status
)
return response
Error Handling:
python
try:
response = agent.run(user_input)
except Exception as e:
# Fallback to human agent
escalate_to_human(user_input, error=str(e))
Step 5: Deploy & Monitor
Deployment Options:
- Dockerize: Containerize your agent for easy deployment
- Cloud Platforms: AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Run
- Monitoring: Track performance, errors, and user satisfaction
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Task completion rate
- Average resolution time
- User satisfaction scores
- Error frequency
- Cost per interaction
AI Agent Chatbot with LangChain
LangChain is the most popular framework for building AI agent chatbots. Here’s why and how to use it.
Why LangChain?
Key Advantages:
- Tool Integration: Easily connect to APIs, databases, and external services
- Memory Management: Built-in context retention across conversations
- Agent Types: Multiple pre-built agent architectures
- Production-Ready: Battle-tested by thousands of developers
LangChain Agent Types
- Zero-Shot React Agent
- Decides which tool to use based on tool descriptions
- Best for: General-purpose agents with multiple tools
- Conversational Agent
- Maintains conversation context
- Best for: Customer support chatbots
- OpenAI Functions Agent
- Uses OpenAI’s function calling
- Best for: Structured outputs and API integration
- Plan-and-Execute Agent
- Plans steps first, then executes
- Best for: Complex, multi-step workflows
Building a Customer Support Agent with LangChain
Complete Example:
python
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, AgentType
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
import os
# Initialize LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=“gpt-4”,
temperature=0,
openai_api_key=os.getenv(“OPENAI_API_KEY”)
)
# Define custom tools
def check_order_status(order_id: str) -> str:
“””Check order status in database”””
# Connect to your database
return f”Order {order_id} is being processed”
def process_refund(order_id: str) -> str:
“””Process refund for order”””
# Connect to payment gateway
return f”Refund initiated for order {order_id}“
def update_customer_info(customer_id: str, info: dict) -> str:
“””Update customer information in CRM”””
# Connect to CRM API
return f”Customer {customer_id} information updated”
# Create tool list
tools = [
Tool(
name=“CheckOrderStatus”,
func=check_order_status,
description=“Check the status of a customer order. Input should be order ID.”
),
Tool(
name=“ProcessRefund”,
func=process_refund,
description=“Process a refund for an order. Input should be order ID.”
),
Tool(
name=“UpdateCustomerInfo”,
func=update_customer_info,
description=“Update customer information in CRM. Input should be customer ID and info dict.”
)
]
# Add conversational memory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key=“chat_history”,
return_messages=True
)
# Initialize agent
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.CHAT_CONVERSATIONAL_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
memory=memory,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True
)
# Run agent
user_query = “I want a refund for order #12345”
response = agent.run(user_query)
print(response)
Advanced LangChain Features
1. Custom Agent Executor
python
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor
# More control over agent behavior
agent_executor = AgentExecutor.from_agent_and_tools(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
memory=memory,
max_iterations=10,
early_stopping_method=“generate”
)
2. Prompt Customization
python
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
custom_prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=[“input”, “chat_history”],
template=“””
You are a helpful customer support agent.
Always be polite and try to resolve issues completely.
Chat History: {chat_history}
Customer Query: {input}
Your Response:
“””
)
3. Error Recovery
python
def handle_agent_error(error):
return f”I encountered an issue: {error}. Let me connect you with a human agent.”
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.CHAT_CONVERSATIONAL_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
handle_parsing_errors=handle_agent_error
)
LangChain Integration Examples
Connect to CRM (Salesforce):
python
from langchain.tools import Tool
import salesforce_api
def get_customer_data(customer_id):
sf = salesforce_api.Salesforce(
username=os.getenv(“SF_USERNAME”),
password=os.getenv(“SF_PASSWORD”)
)
return sf.query(f”SELECT * FROM Contact WHERE Id=’{customer_id}‘”)
crm_tool = Tool(
name=“GetCustomerData”,
func=get_customer_data,
description=“Retrieve customer data from Salesforce CRM”
)
Connect to Database:
python
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain.utilities import SQLDatabase
db = SQLDatabase.from_uri(“postgresql://user:pass@localhost/dbname”)
db_tool = Tool(
name=“QueryDatabase”,
func=lambda query: db.run(query),
description=“Execute SQL queries on the database”
FAQs: AI Agent vs Chatbot
When it comes to knowing AI Agent vs Chatbot, you may ask yourself some questions. Here we have compiled a list of the most relevant questions with answers.
Is ChatGPT an AI agent or a chatbot?
ChatGPT is primarily a conversational AI chatbot. However, when integrated with external tools, APIs, and plugins, it can exhibit agent-like capabilities such as executing tasks and accessing real-time data.
How do AI agents ensure data security?
Security depends on the platform and how the system is implemented. Enterprise-grade AI agents on platforms like Microsoft Azure offer strong, built-in protection.
They include advanced security and compliance features to safeguard sensitive data. Best practices include encryption, access controls, audit logs, and certified compliance standards.
Can AI agents work across multiple channels?
Yes. Modern AI agents are designed to operate seamlessly across multiple channels, including website chat, mobile apps, email, SMS, social media platforms (WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger), voice calls, and internal business tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
How do AI agents handle complex customer requests?
AI agents break down complex requests into smaller, manageable steps. They use reasoning engines to analyze the situation, retrieve relevant data from multiple sources, execute necessary actions across systems, and provide unified responses while maintaining context throughout the process.
Can I integrate an AI agent with my existing CRM?
Yes. AI agents can integrate with popular CRM platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, Microsoft Dynamics, and custom systems through APIs. Integration typically involves connecting the agent to your CRM’s API endpoints and configuring appropriate permissions.
Who are the Big 4 AI agents?
The “Big 4” AI agents typically refer to the leading autonomous agent frameworks: OpenAI Agents, Google DeepMind Agents, Anthropic Claude Agents, and Meta AI Agents. These platforms power advanced reasoning, tool use, and autonomous workflows.
What are the 5 types of agents in AI?
The five main types of AI agents are:
- Simple Reflex Agents
- Model-Based Reflex Agents
- Goal-Based Agents
- Utility-Based Agents
- Learning Agents
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Switching from chatbots to AI agents shows how business automation is evolving in a big way.
It moves companies from reactive information providers to proactive problem solvers.
Key Takeaways
✅ Chatbots are perfect for high-volume, straightforward interactions where information delivery is the primary goal
✅ AI agents excel at complex, multi-step workflows that require autonomy, integration, and end-to-end execution
✅ The choice depends on your specific use cases, budget, and complexity requirements—not on following trends
✅ Many successful businesses use both: chatbots for initial triage and simple queries, AI agents for complex resolutions
✅ Building AI agents is increasingly accessible with frameworks like LangChain and resources available on GitHub
Need expert guidance?
Our team specializes in designing and deploying custom AI agents tailored to your business needs. Contact us for a free consultation and discover how AI agents can transform your operations.
Reference



